Executive Summary
This case study provides a detailed description of Coincento – an entity-, bank-, and technology-agnostic solution that enables:
- seamless integration with the banking infrastructure based on ISO 20022, capitalising on and requiring minimal modifications to the existing banking platforms,
- cross-network interoperability and efficiency across digital finance,
- improved data transparency and
- end-to-end traceability for the use case flow and further process mapping, reconciliation, streamlined internal audits and regulatory reporting.
Coincento was developed by the Exactpro team during the Swift Hackathon 2025. It was shortlisted among the six Technical challenge finalists of hackathon and awarded an honourable mention at the hackathon final during Sibos Frankfurt. The solution leverages the Exactpro team’s expertise at the intersection of software testing and development of complex distributed financial systems, distributed ledger technology (DLT) and emerging technologies.
Enhancing cross-border payments with APIs and standardisation
Compared to other solutions available on the market, Coincento offers enhancements in the following areas:
- Payment initiation
- Back-office processes
- Payment tracking and status
- Reconciliation and reporting
- Product innovation
- Interlinking payment systems
Some of these goals were met with the use of the ISO 20022 standard that contributes to enhanced data and efficiency, streamlined operations, deeper customer insights and stronger fraud prevention.
Objectives and industry considerations behind Coincento
- Smart contracts for automation for the complex workflows, such as cross-border payments and their reconciliation.
- ISO 20022 and DLT process automation synergy and benefits for easy reconciliation processes.
- Compliance checks automation, minimising human oversight while ensuring regulatory adherence.
The use of DLT as an alternative to potentially improving the efficiency of cross-border payments:
- lower costs (by removing intermediaries like correspondent banks)
- greater access (via enabling many participants to connect directly)
- higher speeds (via using standard formats and fewer intermediaries)
- better transparency (everyone sees the same record on the shared ledger)
- Compared to traditional systems, DLT enables near-instantaneous transaction settlement, reducing delays.
- DLT’s consensus mechanisms ensure accurate, tamper-proof records across distributed nodes, minimising errors in real-time data management.
- Permissioned DLT enhances transparency and immutability, improving transaction data quality for regulatory compliance, such as anti-money laundering (AML) and know-your-customer (KYC) requirements.
- DLT ensures the ability to provide transparent access to data, increasing accountability and reducing fraud.
Coincento solution
The word ‘Coincento’ is a blend of the words ‘coin’ and ‘concento’ – a Latin-derived musical term that can translate as ‘harmony’ or ‘agreement’. In Italian, ‘cento’ also means ‘a hundred’, which, combined with ‘coin’ represents the solution's mission to harmonise fiat currencies and digital coins into one well-functioning ecosystem.
Key concepts of the solution
Coincento (see Figure 1) is a DLT-based platform that enables seamless integration with the banking infrastructure based on ISO 20022, capitalising on and requiring minimal modifications to the existing banking platforms. It is an entity-, bank-, and technology-agnostic solution integrated with a transactions dashboard for ongoing monitoring, analysis and operational flow management as well as post-transaction analytics. This provides participants with a high level of transaction visibility. The use case flow presented in this case study demonstrates end-to-end traceability – a transaction attribute and product feature vital for further process mapping, reconciliation, streamlined internal audits and regulatory reporting.
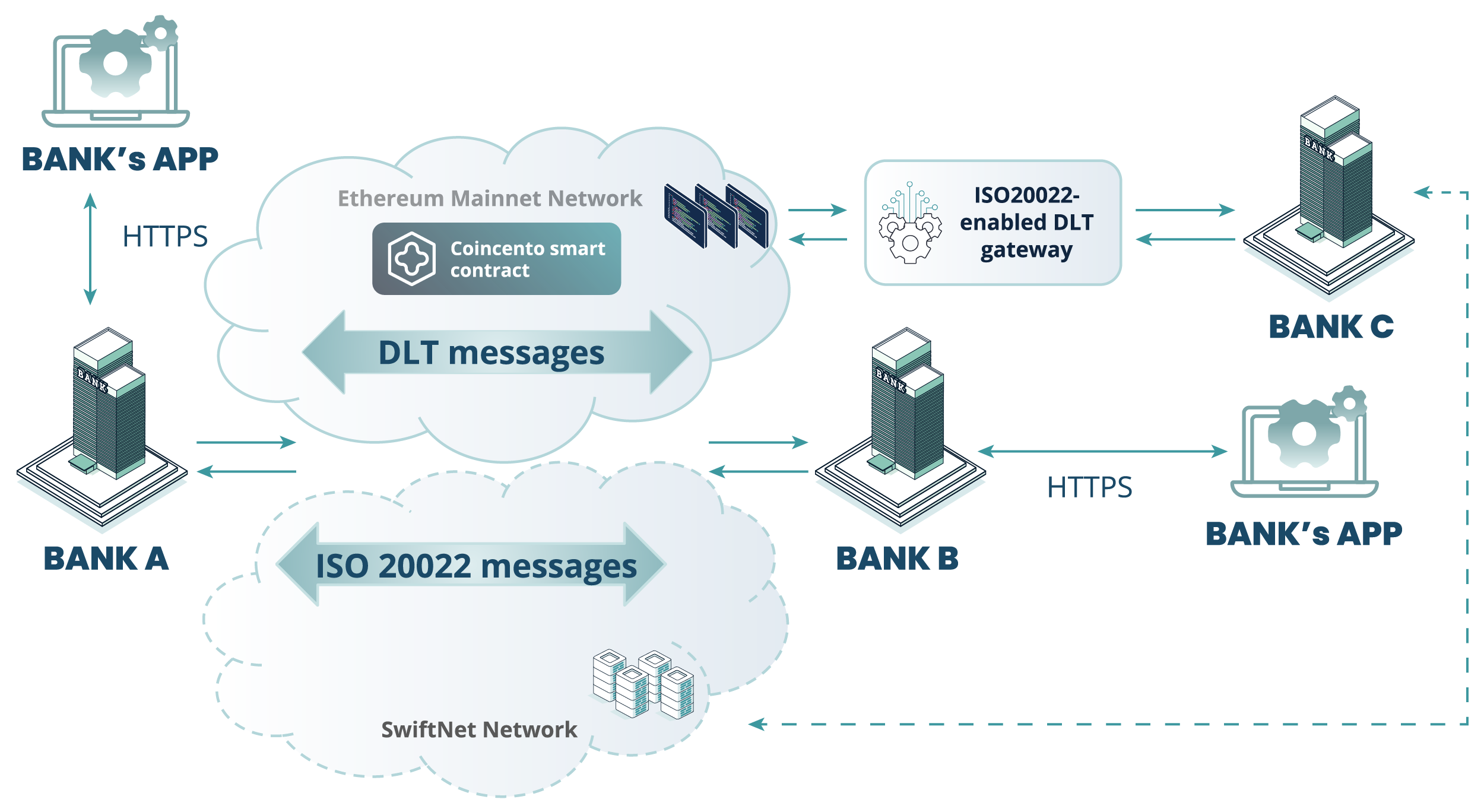
Figure 1. High-level schema of the Coincento solution
Solution architecture design
Coincento’s main components are: a Bank’s Client App, a Core Banking Application and an Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) blockchain with customised smart contracts that enable the creation and execution of smart contracts within the Ethereum Mainnet Network.
Bank’s App – a banking application designed for mobile devices or computers that allows customers to access and manage their bank accounts and financial services digitally.
Ethereum Mainnet Network – an Ethereum-based blockchain network where real-value transactions and smart contracts are executed using Ether (ETH). A decentralised platform for operating tokens through a secure network of nodes.
Smart contract (similar to ERC-1155) – a customised ERC-1155 multi-token standard. A single deployed contract that may include any combination of fungible tokens, non-fungible tokens or other configurations (e.g. semi-fungible tokens). The implementation extends the existing functions of the ERC-1155 token in order to accommodate the proposed transaction flows.
DLT messages – the data and transactions broadcast, recorded, and shared across the decentralised network of nodes. The messages contain information about the transaction details, smart contract updates or state changes, which are validated and added to the ledger in accordance with the network’s consensus rules.
Core Banking Application – an application used by banks to manage their core operations and customer-facing services. It ensures real-time updates, data management, and integration with other banking systems.
SwiftNet Network – Swift, an advanced IP-based messaging platform. SwiftNet comprises services and products that enable customers to communicate mission-critical financial information and transactional data securely and reliably.
ISO 20022 messages – this represents the capability of banks to exchange payment, cancellation, and reconciliation instructions using a standardised messaging format – ISO 20022, for structured financial communication over the Swift network.
ISO 20022-enabled DLT Gateway – a DLT Gateway with a set of custom API functions for small-scale banks which choose not to create a separate application in order to use the same capabilities as Ethereum Mainnet Network participants. This component is used for integration purposes.
Coincento architecture (Fig. 2) offers clients easy review and management of funds, with all actions reflected in their transaction history. At the same time, it equips banking operators with transaction management, message workflow tracking and reporting tools.
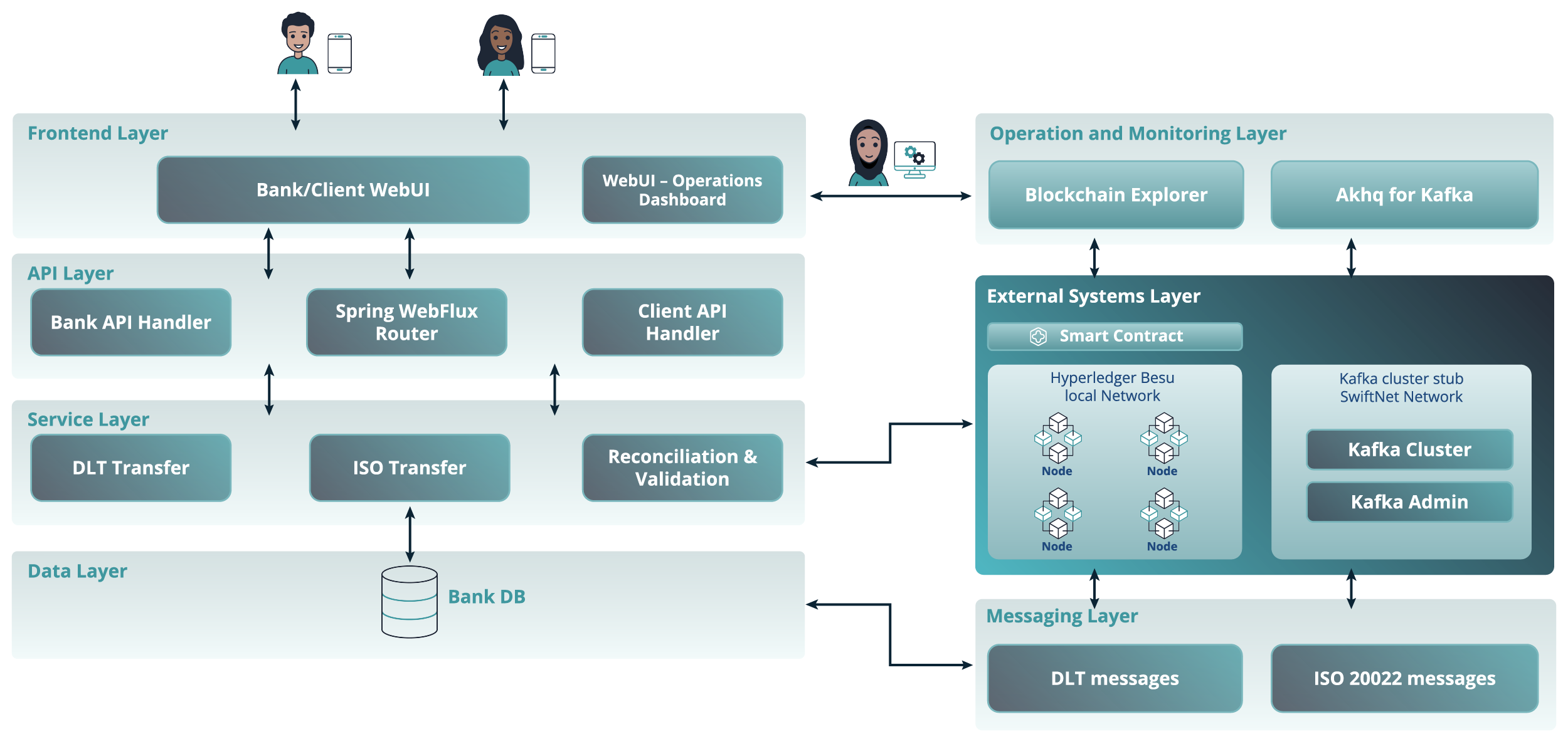
Figure 2. The Coincento architecture design
Coincento network schema
The following schema (seen in Figure 3) reflects the Coincento network as configured for the Swift Hackathon 2025 demo environment.
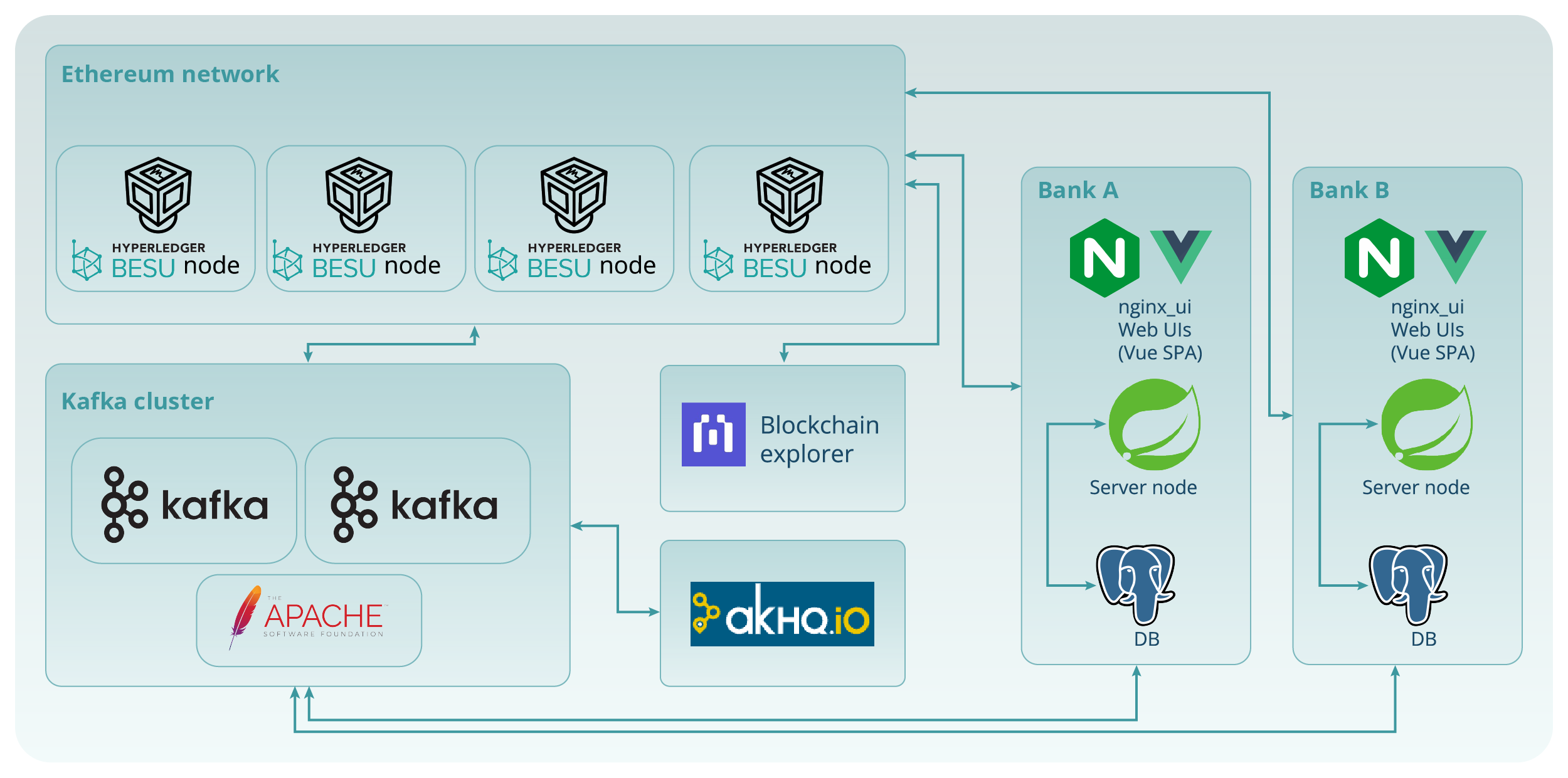
Figure 3. The Coincento network schema
Key Coincento platform features
Speed and transparency
- Leveraging ISO 20022 features to enhance transparency
- Using smart contracts to automate operational and reconciliation processes
- Accelerating payment speed by applying the structured and high-quality data standard
- Minimising errors at source
- Allowing straight-through processing of the payments (including cross-border ones)
Interoperability and seamless payments
- Supporting the enhanced ISO 20022 standard
- Seamless integration with the existing banking infrastructure
- Interoperability with blockchain networks
- Supporting integration with other monitoring solutions
- Real-time access for the regulators
Operability and compliance
- Legal entity-, bank-agnostic
- Integrated with the transactions dashboard for further analysis
- Use cases flow management and analytics
- Enabling transaction visibility across participants
- End-to-end traceability for each use case flow and further reconciliation
- Сompliant with regulations
Platform design
- DLT provides a transparent, tamper-proof ledger for all transactions, ensuring auditability and regulatory compliance
- DLT's consensus mechanism enables near-instantaneous transaction settlement and real-time payment processing
- ISO 20022-enabled messaging
- Enables interoperability with traditional systems and other DLT networks
Key design features of the Coincento token
Operation within a compliant, permissioned framework

Elimination of the need to ‘approve’ individual token contracts separately

1:1 exchangeability with a base token (like USDC)

Safe transfer functions

Alignment with ISO 20022 standards for messaging

Enabling automation of complex messaging workflows

Flexibility of the smart contract designed to support multiple types of base tokens
Key User Interface features
Minimalistic & intuitive design
- Clean layouts with clear navigation paths reduce cognitive load for all user types
- Simplified interaction patterns support intuitive navigation, even for first-time users
Real-Time dynamic dashboards
- Live updates on transactions, balances and status changes
- Future enhancement: AI-driven notifications and predictive insights to guide user decisions proactively
Advanced transaction management
- Transaction filters & search to quickly locate transaction data using filters such as date, amount, status and other relevant criteria
- Color-coded feedback system: green for completed payments, red for rejects and neutral for informational data
- Contextual feedback: real-time confirmation messages as users interact with the system
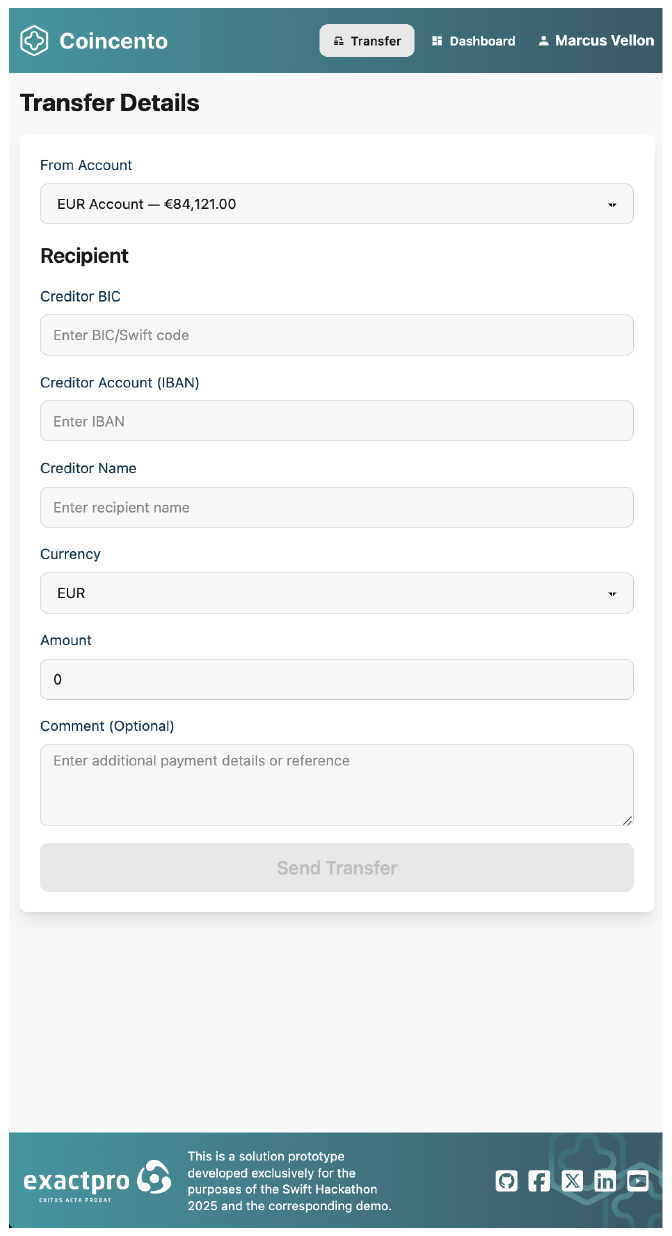
Figure 4. Coincento UI example
Future-ready by design: Coincento is built to expand with high-impact features
- Integration with CBDCs to support transactions with CBDCs, enabling seamless integration with digital fiat currencies issued by central banks
- Privacy implementation to protect sensitive banking data while maintaining regulatory transparency and auditability
- Integration with core banking systems with minimal modifications to banking infrastructure
- Programmability embedded at the account level to support programmable payments
- Well-rounded test strategy and comprehensive test framework
- API gateway for DLT cross-chain interoperability with public blockchains for broader stablecoin and DeFi integrations
- Dynamic dashboards, AI-driven notifications
- LLM integration
- Expansion to support tokenised assets to facilitate tokenisation of real-world assets (e.g securities, real estate) for trading and settlement on the DLT platform
- AML and KYC Integration
- Automated FX conversion layer
Key business cases
This section outlines key tokenised payment scenarios demonstrating how digital assets will be securely issued, transferred and reconciled within the DLT network. Each use case illustrates a specific operational flow designed to ensure regulatory compliance, interoperability with ISO 20022 messaging standards and seamless integration with traditional core banking systems.
Use case 1: Token transfer between banks (same token – USDC)
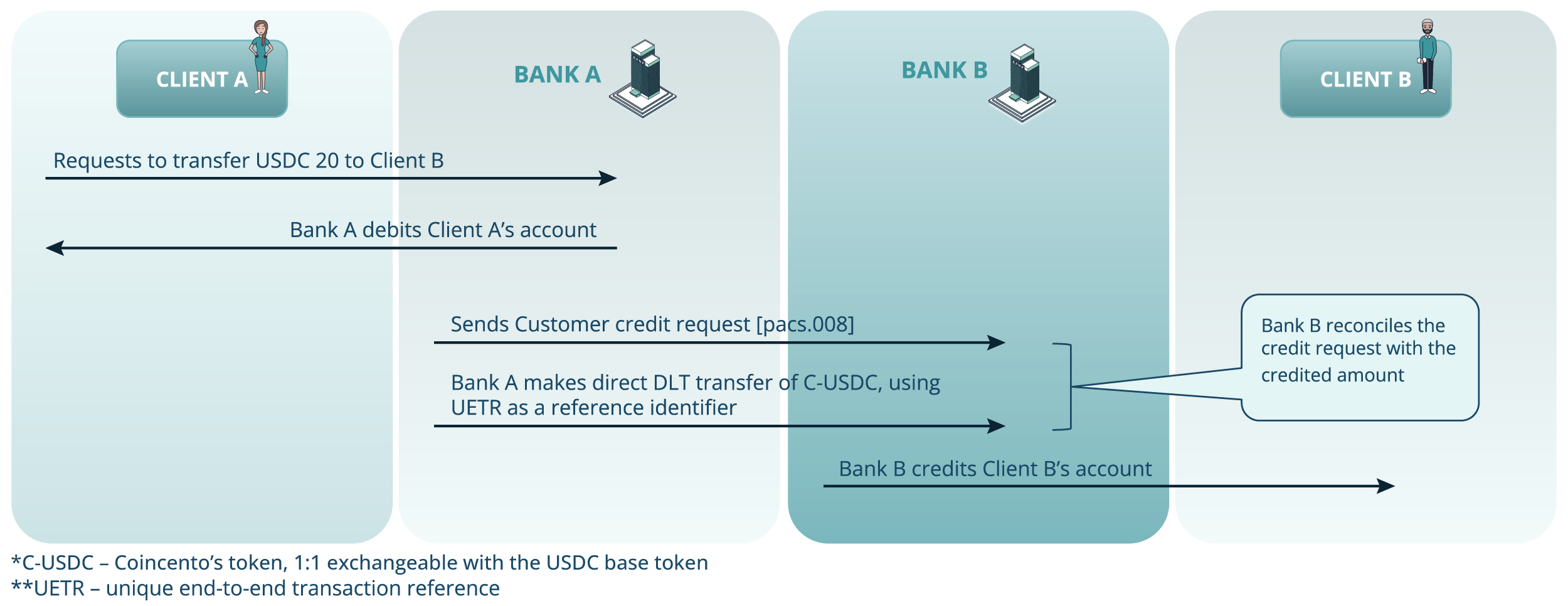
Figure 5. The scenario demonstrating a Token Transfer Between Banks (same token – USDC)
- Client A initiates a USDC transfer to Client B.
- Bank A debits Client A’s account.
- Bank A sends a pacs.008 customer credit request message initiating payment instruction.
- Bank A makes a direct DLT-base transfer, referencing the UETR to ensure traceability. S-USDC token is used to perform the transfer.
- Bank B reconciles the credited amount with the incoming message. Bank B credits Client B’s account, completing the transaction.
Use case 2: FX-based token transfer (EUR→USDC)
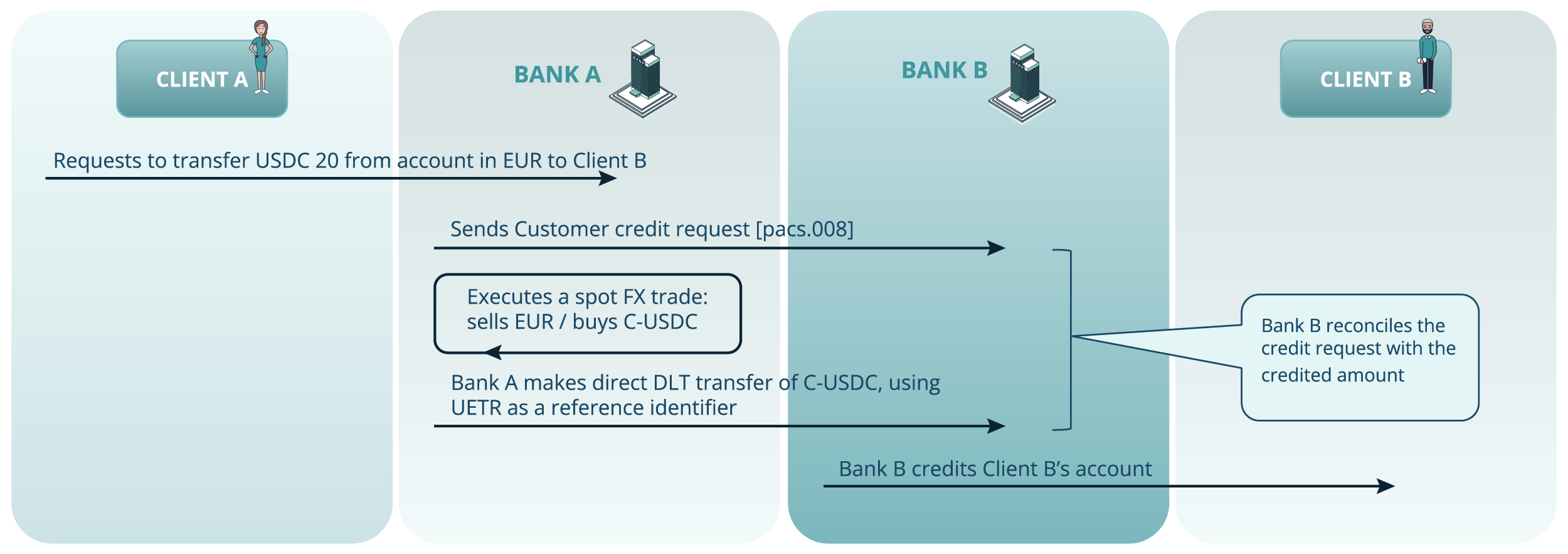
Figure 6. The scenario illustrating a FX-based Token Transfer use case
- Client A requests a cross-currency fiat-to-token transfer. Domestic currency for Bank A is USD, for Bank B is EUR.
- Bank A sends a pacs.008 customer credit transfer message to Bank B initiating the payment.
- Bank A performs a spot FX trade, converting the necessary amount of EUR into USDC (S-USDC).
- Bank A then executes a direct DLT transfer of S-USDC to Bank B, referencing the UETR.
- Bank B reconciles the received token amount on DLT with the payment instruction.
- Bank B credits Client B’s account with the required amount of USDC, completing the cross-currency token transfer.
Use case 3: Transfer cancellation request
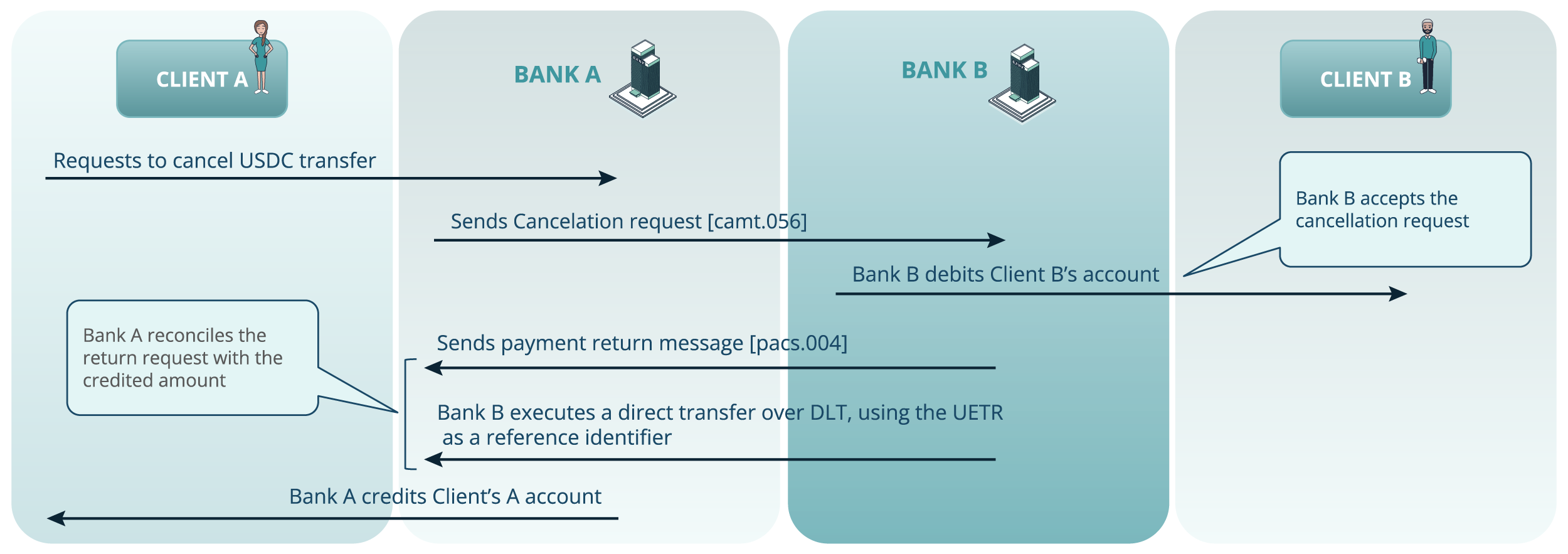
Figure 7. The scenario illustrating a Cancellation request use case
- Client A initiates a cancellation request.
- Bank A sends a camt.056 cancellation message to Bank B.
- Upon acceptance, Bank B debits Client B’s account.
- Bank B sends a pacs.004 return message to Bank A.
- Bank B performs a reverse DLT transfer back to Bank A, referencing the original UETR.
- Bank A reconciles the return request with the credited amount and recredits Client A’s account.
Use case 4: Token withdrawal
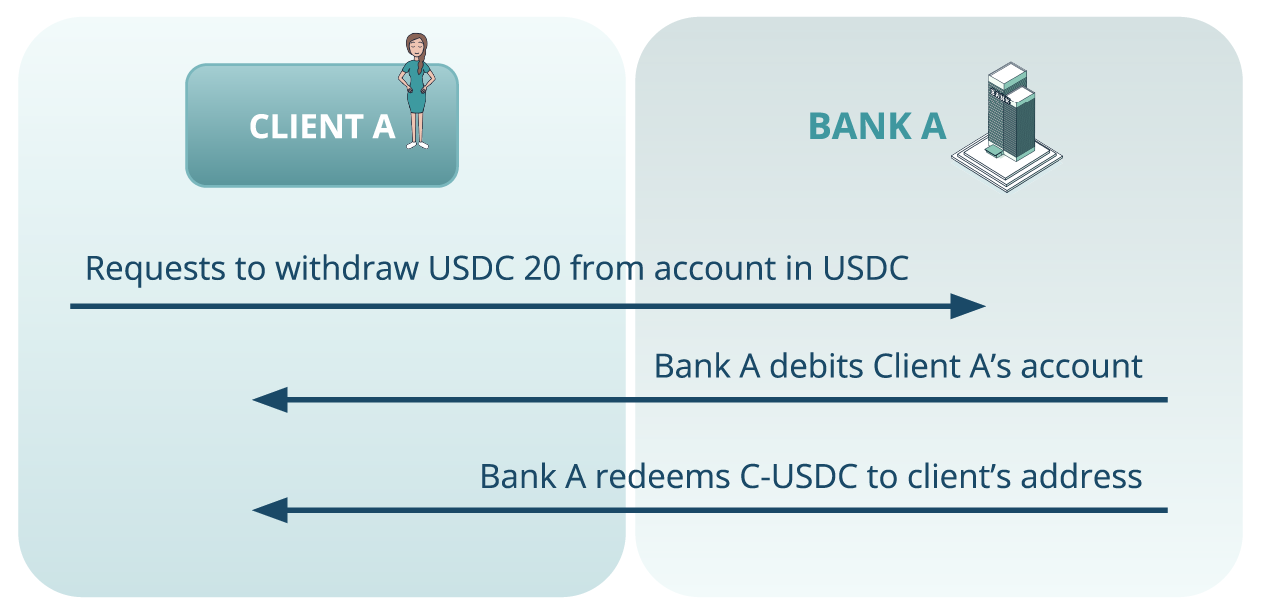
Figure 8. The scenario illustrating a token withdrawal use case
- Client A requests a withdrawal of USDC.
- Bank A debits the client’s fiat account and redeems the equivalent amount of S-USDC, converting it into USDC and transferring it to the external DLT client’s address. This finalises token withdrawal from the bank-controlled infrastructure.
Coincento demo
The demo below illustrates the business use case covering a token transfer between banks.
Financial industry impact
- Legal entities including Banks prefer using ISO 20022-compliant assets for seamless integration.
- ISO 20022-enabled DLT Gateway with rich API capabilities also allows direct integration with core banking systems to maintain the existing operation process at the entities.
- The regulatory landscape in FinTech is focused on transparency and traceability. ISO 20022’s structured data fields help meet compliance requirements and, therefore, the Coincento solution is aligned with the ISO standard.
- The automation of the compliance reconciliation process reduces human oversight while ensuring regulatory adherence.
- In comparison with traditional slow and costly payments, the solution helps to reduce the processing time and have room for offering low-cost support for transactions.
- Lower compliance and reconciliation costs due to reduced compliance and, as a result – cutting the costs for manual investigation of these errors.
- DLT’s near-instantaneous settlement frees up capital trapped in settlement cycles, enabling reinvestment.
- Reduced operational risks from manual processes and errors in transaction processing, reconciliations, and compliance checks.
- DLT’s immutable ledger prevents unauthorised changes to transaction data and minimises fraud and errors.
- DLT’s automated compliance reduces regulatory non-compliance risks (Coincento’s ISO 20022 integration ensures standardised, compliant data flows).
- Transparent ledger offers regulators real-time access to transaction data, reducing compliance gaps.
- Settlement finality reduces disputes over transaction status.
Key takeaways
Coincento represents a significant advancement in bridging traditional financial messaging standards with distributed ledger technology (DLT), delivering a unified platform for cross-border payments and token-based transfers. By seamlessly integrating ISO 20022 message flows with DLT-based token instructions and smart contract automation, the architecture addresses longstanding challenges in interoperability, manual intervention and reconciliation. The key outcomes achieved through this design are summarised below, highlighting improvements across process automation, real-time visibility, transparency, data integrity and operational efficiency.
Process automation
The solution automates key transactional activities by integrating ISO 20022 message flows with DLT-based token instructions. Identifier mapping between traditional financial data and token-related fields will be fully automated, reducing the risk of manual errors. Additionally, FX conversion and payment transfers are executed as part of the defined ruled-based workflow, eliminating the need for separate processing and reconciliation steps.
Real-time accuracy
An event-driven architecture supports real-time tracking of the transfer status across the entire transaction lifecycle. Each transfer is linked to a UETR for accurate tracking and up-to-date reconciliation. The ISO 20022-enabled DLT infrastructure ensures that authorised parties can view the current state of each transaction instantly, while maintaining data privacy and platform-level control.
Transparency
Coincento enables the stakeholders (banks, their clients and regulators) to access and audit transaction data in a clear, verifiable manner. The solution design ensures controlled, auditable access to transaction records, their messaging workflows, aligning with its transparency objective.
Data integrity
The solution ensures that transaction data remains accurate, consistent and tamper-proof throughout its lifecycle. The DLT architecture and smart contract automation safeguard data integrity of the transaction data, while addressing banking-specific needs.
Operational efficiency
Coincento has a role-specific UI, tailored to client needs, sending/receiving banks, streamlining their respective actions within the transfer and settlement workflows. By consolidating token operations, including FX handling and settlement logic, into a single platform, the solution aims to reduce operational fragmentation and to improve processing speed and transparency.
References
1 Global Financial Markets Association (gfma) (2025) ‘Joint Trades Publish Report on the Impact of DLT in Capital Markets’, gfma, 19 August 2025. https://www.gfma.org
2 Zetzsche, D.A., Anker-Sørensen, L., Passador, M.L., Wehrli, A. (2022) BIS Working Papers (No 1015). DLT-Based Enhancement of Cross-Border Payment Efficiency – a Legal and Regulatory Perspective. Bank of International Settlements. https://www.bis.org/publ/work1015.pdf
3 The European Central Bank (2025) ‘Tokenisation and DLT’, European Central Bank | Eurosystem. https://www.ecb.europa.eu
4 Paridon, P.P., Smith, J. (2024) ‘Distributed Ledger Technology: A Case Study of The Regulatory Approach to Banks’ Use of New Technology’, Bank Policy Institute, February 1, 2024. https://bpi.com)
With Coincento