Date:

By Alyona Bulda, Head of Global Exchanges, Technology SVP, Exactpro
Due to a combination of factors, measures that organisations take to ensure market data systems integrity and resilience should receive increased attention this year.
The Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA)1 – an EU regulation sector-specific to financial institutions, including the market data providers and the technology networks supporting their infrastructures – is one of these factors. In the context of a “highly interconnected global financial system,” it mandates that every individual financial infrastructure “duly consider ICT risk,” and aggregate relevant best practices to make its systems more resilient to cyber threats and operational disruptions. This includes testing for data corruption or loss and other “technical flaws that may hinder business activity,” among possible mechanisms to prevent or mitigate system failures. Another reason to turn the spotlight on market data solutions resilience is the European Securities and Markets Authority (ESMA) ongoing plans on developing a pan-European consolidated tape (CT) system.2
In view of these major developments – and more ongoing change happening across the Atlantic (e.g. OPRA’s Dynamic Load Balancing Proposal)3 – we are at a point where it becomes crucial to coordinate the transformation and innovation efforts, to ensure the quality and reliability of market data solution integrations on the individual infrastructure level, as well as on a global scale. For developing systems like European consolidated tape, it is important to consolidate the industry’s best practices to embed quality into the new solution from the outset.
As we know, market data systems are tasked with quote aggregation from trading venues, processing – including the accompanying data enrichment – and dissemination to all market participants relying on them for price discovery (including BBO) and index formation, leading to well-functioning markets and informed and timely decision-making. Understanding the unique architecture of market data solutions and surrounding components is key in setting up efficient operation and the ability to demonstrate full compliance, both of which are contingent on thorough testing. Taking into account the dynamic nature of electronic trading and the structural complexity of the infrastructure and its interconnected process flows, a market data system testing approach should be able to factor in the following challenges:
Functional requirements and business-related challenges
- Accurate processing of quotes collected via multiple sources with different transportation protocols and recovery mechanisms.
- Coexistence of disparate and complex data formats and protocols.
- Varying data sources, normalisation and enrichment mechanisms.
- Permutations of the subscription layers and requests leading to a high number of consistency checks within streams.
- Increased volumes of historical data due to multiple sources and enrichment mechanisms.
- Operability, maintainability and system monitoring challenges in such distributed systems.
- Adherence to strict regulatory requirements.
Infrastructure and non-functional requirements-related challenges
- High data volumes prone to fluctuations
- Ultra-low latency real-time performance, synchronization across the infrastructure
- Possibility of data loss, corruption or interrupted delivery
- Integrations with surrounding systems
FPGA-related challenges
The ultra-low-latency handling of market data is often made possible via the use of FPGA technology. Its high cost and distinctive architecture incur another set of unique challenges: cost efficiency of the environments (affecting test environments), their maintainability and operability, additional complexities in test case development.
Introduction of distributed technologies and emerging asset classes further complicate data structures and underscore the importance of well-tested data aggregation, processing and dissemination mechanisms.
However, in a complex distributed system, it is essential to not only account for all possible challenges separately, but understand the possibility of hidden interdependencies that will only reveal themselves at the intersection of functional and non-functional system characteristics. This interrelation is the reason for system non-determinism arising under specific non-functional conditions. These conditions should be thoroughly explored during testing, to minimise the chance of their occurrence in a production environment:
- Any complex system sustains a certain level of concurrency (race conditions), during which the state of a message or component can get corrupted (they can usually be revealed when a high-frequency load is applied).
- Production-level randomisation adds to scenario complexity and system components may behave differently in such complex scenarios combined with load conditions.
- Integer overflow in certain scenarios – the fields in the statistics messages that are constructed via calculation and fields representing incremental identificators can overflow when system events leading to these cases are generated repeatedly.
- Dynamic mass events in the source upstream system or in the ticker plant which happen during the Daily Life Cycle (DLC), i.e. opening, closing, auction uncross, etc. The state of the system when these DLC events happen should be verified with the load applied against the system.
Effective assessment of market data solutions quality should take the form of a hybrid approach featuring two types of environments – exchange simulators (specially modelled digital twins) and dedicated test environments (see Fig. 1). They can be used in parallel or independently during appropriate project stages or current circumstances. For instance, simulators are especially valuable at early stages (when the system is not yet ready for integration with upstream systems), but also during temporary maintenance of upstream systems or presence of blocker bugs in them. This approach also provides unparalleled value for extensive non-functional testing exploration. Load testing activities tend to require powerful simulators and/or historical data replay tools because dedicated upstream test environments may not be able to withstand the required load. Simulators are more reliable when stable performance benchmarking is needed. However, the ability to use dedicated test environments is the best option for integration and user acceptance testing.
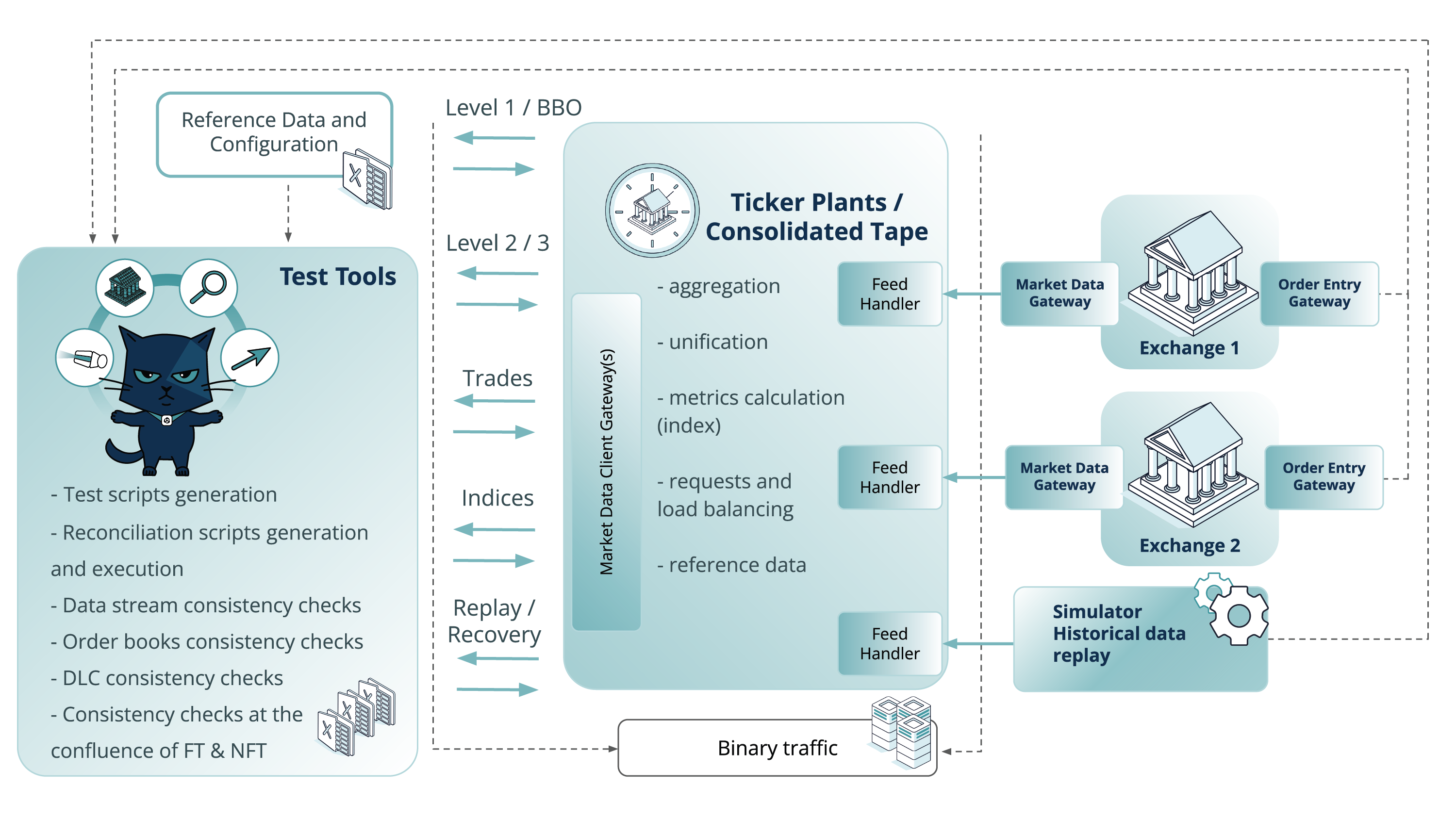
Fig.1 High-level illustration combining the test approaches to achieve Market Data Solutions Resiliency
The testing activities should also be supported by a data-first model-based testing strategy. It is a data-driven practice that helps produce a test suite fully accommodating the complexity of a large-scale financial system and enables the development and maintenance of market simulators. In turn, system modelling paves the way for pervasive automation, including the use of Generative AI for test case development and test library optimisation – to deepen the level of system exploration and help free more human resources for more cognitively demanding tasks, and help create an extensive and yet highly resource-efficient test library with deep system coverage. Such AI-enabled model-based assessment of market data systems quality is an efficient way to enhance their functionality, resilience and performance, while facilitating results analysis, transparency and regulatory compliance.
In the context of widespread transformation impacting the market data technology landscape, increasing the stability of this segment of the financial ecosystem is paramount for its overall health. Thorough testing provides information about the system and its behaviour, insights into potential risks, and helps manage those risks and act accordingly and commensurately to the information received – making better-informed, more precise decisions, ensuring that the system is prepared for adverse conditions. Based on the outcomes of an objective quality assessment, institutions can adjust strategies, and regulators can implement policies to mitigate systemic risks.
Comprehensive testing can act as a preventive measure by simulating adverse conditions and providing the opportunity to learn from the outcomes early on, it reduces the likelihood of financial instability and protects separate systems and the broader economy from cascading effects.
To access the full set of recommendations and a detailed description of the industry-proven AI Testing approach for market data solutions, please visit Exactpro’s Market Data Systems Testing case study.